What is the main difference between open and closed circuit cooling towers?
The difference between the two systems lies in the different type of circuit exploited to cool the process fluid.
- Open-circuit (or open-loop) cooling tower: water flows downward through a fill material, distributing itself in a thin film. Fans inside the tower draw in cold air from outside, which flows through the fill material, in contact with the “hot” water. A very small part of the water evaporates, absorbing heat from the air, while the remaining part cools and is collected in a basin for reuse. Video of open-circuit evaporative tower operation.
- Closed-circuit (or closed-loop) cooling tower: the “hot” water from the industrial process does not come into direct contact with the air, but instead circulates in a closed circuit within the tower. A secondary fluid flows in a separate circuit, adjacent to the primary circuit: this is “sprayed” onto the smooth-tube primary circuit and removes the heat of the liquid contained therein. Contact between the air, drawn by the fans, and the sprayed water causes the latter to cool in turn. Video of closed-loop evaporative tower operation.
In summary, open-circuit cooling towers bring process water into direct contact with air, allowing part of the water to evaporate and dissipate heat. They are simple solutions suitable for large flow rates, provided that continuous water treatment is ensured. Closed-circuit cooling towers, on the other hand, keep the process fluid (typically water and glycol) isolated inside coils: the evaporating water belongs to a separate secondary circuit. This reduces maintenance costs and preserves the purity of the process fluid—an alternative to an open-circuit tower combined with a heat exchanger. It is the ideal choice for sensitive sectors such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and data centers.
How do you choose between an open-circuit and a closed-circuit cooling tower? By analyzing the specific requirements of the process, the equipment to be cooled, the available space, and other relevant factors. Moreover, using thermal simulation and resource-optimization software makes it possible to identify the most efficient solution based on climate conditions, actual loads, and the project-specific return on investment.
En savoir plus

Cooling Towers: What They Are, How They Work, How to Maintain Them
How evaporative cooling towers work, performance, internal components, industrial and HVAC applications. Water maintenance and treatment.
Cooling Towers: Components and Materials
The quality of the water to be cooled significantly affects both the choice of constructive materials and fill pack material.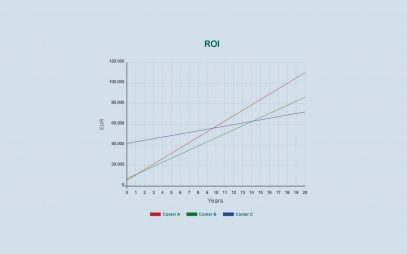
Resource and Efficiency Optimization of Cooling Systems: How to Assess It
The comparison between different cooling technologies: a calculation software can now fulfill this task based on real climatic data.Produits associés

PME-E Open-Circuit Evaporative Cooling Tower
A light and non-corrodible open-circuit evaporative cooling tower: process industry and HVAC operators will be able to count on its multiple versions and ease of transport and installation.

MCC Closed-Circuit Evaporative Cooling Tower
Some industries need to keep the chemical-physical characteristics of the process fluids unchanged: in these cases, MCC closed-circuit evaporative cooling tower joins the game. Possibility to work in free-cooling mode. MCC-EC version available with electronically controlled fans.

MITA Control System
MITA Control System allows programming and modulating cooler’s performances during its operations in a very simple way. Electricity use optimization is granted.
Newsletter
Subscribe to MITA newsletter and stay updated on technical solutions for industrial and civil cooling and get to know our offer.